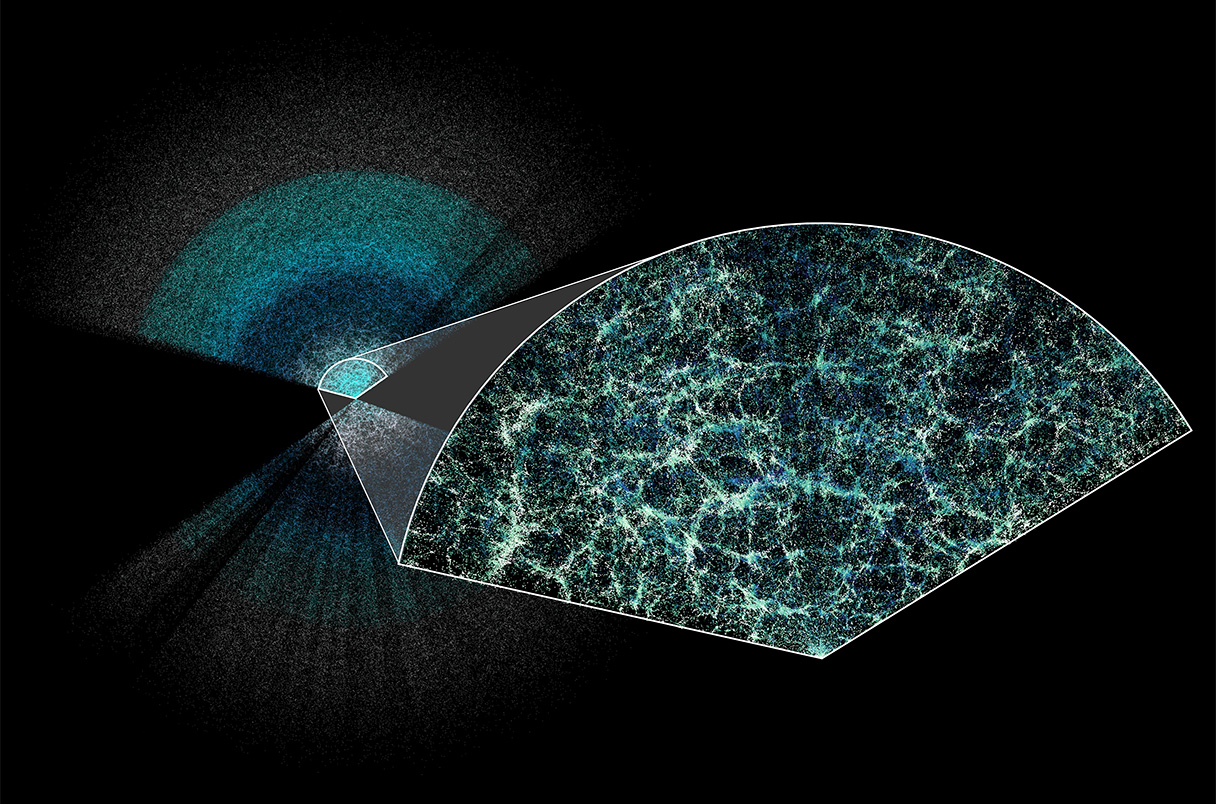
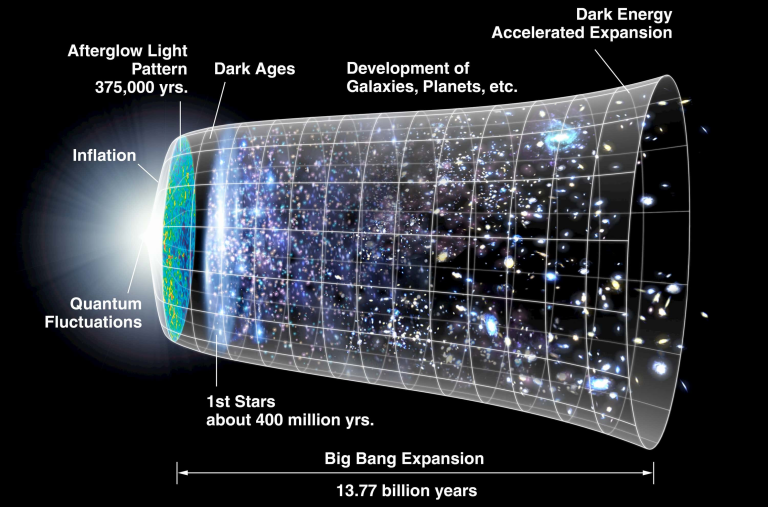
Dark energy analysis has emerged as a prominent focus in astrophysics research due to its crucial role in understanding the universe’s expansion. Recent findings from the international Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) collaboration, which includes notable contributions from Harvard scientists, suggest that this enigmatic force, often referred to as a ‘cosmological constant’, might be changing over time. This revelation raises significant questions about the current models of cosmology and the enduring nature of dark energy’s effects on the expansion of the universe. By employing an extensive 3D map crafted from data on over 14 million galaxies, researchers are gaining valuable insights into how dark energy influences cosmic evolution. As the DESI collaboration continues to unveil new dark energy findings, it solidifies our understanding of the cosmos and challenges existing theories by providing a deeper glimpse into the fundamental forces that shape our universe.
The discourse surrounding the investigation of dark energy and its implications for cosmic dynamics is gaining traction among scientists and enthusiasts alike. Terms such as ‘accelerating universe expansion’ and ‘mystifying energy components’ characterize alternative discussions in this captivating field. Through collaborative efforts like the DESI initiative, researchers are revealing intricate details of how unseen forces impact the structure and growth of the cosmos. This collective analysis not only sheds light on the fundamental nature of dark energy but also integrates findings from various astrophysics research ventures, strengthening our comprehension of the universe’s past, present, and future. As we delve deeper into this area, the quest to decipher the mysteries of dark energy remains a pivotal pursuit in the ongoing exploration of cosmic phenomena.
The Role of DESI in Unraveling Dark Energy
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) has emerged as a pivotal tool in astrophysics research, unraveling the enigmatic forces that drive the universe’s expansion. As it maps the cosmos, DESI focuses on dark energy analysis, revealing crucial insights about how this mysterious phenomenon influences the universe’s growth over billions of years. The collaboration behind DESI involves over 900 researchers worldwide, including astronomers from the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics, all working together to deepen our understanding of this elusive aspect of cosmology.
Through its high-precision measurements and revolutionary techniques, DESI is crafting the largest 3D map of the universe, which captures the distribution of over 14 million galaxies and quasars. This mapping not only helps with dark energy findings but also provides a wealth of information that feeds into our understanding of the universe’s overall structure and evolutionary history. Insights gained from this analysis challenge existing theories about the cosmological constant, suggesting that dark energy’s effects may not be static but evolving instead.
Implications of Weakening Dark Energy
Recent findings from the DESI collaboration open up new avenues for understanding the future of the universe. The analysis indicates a potential decrease in the strength of dark energy, prompting scientists to consider a re-evaluation of the standard model of cosmology. If dark energy continues to weaken, it could significantly alter the trajectory of the universe’s expansion, raising profound questions about its eventual fate. This insight integrates with previous studies on universe expansion, which viewed dark energy as a consistent force driving acceleration.
As researchers probe deeper into the cosmos, they find that the balance between dark energy and matter is critical to understanding the universe’s destiny. The implications of a changing cosmological constant, posited by the DESI data, suggest that we must reassess theoretical frameworks that have long guided astrophysical research. Emphasizing the importance of continuous observation, these findings highlight the need for dynamic models that keep pace with the universe’s evolving nature.
The Data Revolution in Astrophysics
The launch of DESI marked a transformational shift in how astrophysicists analyze celestial data. By generating a comprehensive dataset that includes detailed information about millions of galaxies, DESI invites both professional astronomers and amateur astrophysics enthusiasts to explore and analyze cosmic phenomena. This democratization of data empowers a broader community to contribute to ongoing research, making the study of dark energy and the universe’s expansion accessible to a wider audience.
As part of its commitment to education and public outreach, the DESI collaboration has enabled the release of Data Release 1, allowing users to interact with raw data and contribute to various research projects. This innovative approach not only enhances transparency in scientific research but also catalyzes new discoveries in galaxy evolution and the structure of the cosmic web. Desi’s influence extends beyond mere data collection, paving the way for collaborative efforts that may redefine our understanding of cosmic patterns.
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations and Cosmic Rulers
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations (BAOs) are essential features in the universe’s structure that serve as standard rulers for cosmological measurements. These oscillations arose from sound waves in the early universe, leaving detectable imprints on the distribution of galaxies we observe today. By analyzing these patterns, DESI provides valuable insights into the evolving role of dark energy and offers an observational backdrop to understand the physics of the universe’s acceleration.
Understanding how these BAOs have changed over time is crucial for deciphering the evolution of dark energy and matter density. The intricate relationship illustrated by BAOs gives researchers the tools to measure distances across vast cosmic distances accurately. As astrophysics research evolves, the ongoing studies of these patterns will be pivotal for predicting how the universe will expand in the future, further anchoring our perception of dark energy’s role.
COSMIC MAPS: The Future of Astrophysical Research
The ambitious mapping efforts spearheaded by the DESI collaboration represent a new frontier in astrophysical research. With constant updates to its extensive 3D universe map, DESI continuously refines our understanding of cosmic structures and the influence of dark energy. As the instrument captures more data, it enables researchers to conduct detailed analyses that reveal insights previously hidden in the vastness of space.
This detailed mapping serves not only to facilitate dark energy analysis but also assists in a broader range of studies, including galaxy evolution and the intricate pattern of the cosmic web. Each mapping campaign contributes to a comprehensive narrative of the universe’s lifecycle, enhancing our grasp of the challenges posed by quantum gravity and other complex phenomena. As researchers delve into the data, they set the stage for groundbreaking discoveries in how we understand the interrelation between cosmic forces.
Collaboration: Driving Global Astrophysics At Its Best
The DESI collaboration epitomizes the power of teamwork in modern astrophysics. Global cooperation among researchers provides a unique platform for sharing knowledge and resources, fostering innovation in tackling complex cosmic questions. Through joint ventures like this, advancements in understanding dark energy and the universe’s expansion are accelerating, showcasing the collective effort that drives the scientific community forward.
With institutions coming together from over 70 countries, the diverse perspectives and expertise combined in the DESI project yield insights that stand to redefine our scientific landscape. This collaborative effort engenders a rich exchange of ideas, from algorithm development to public outreach strategies, illustrating the importance of shared knowledge in the quest to unravel the mysteries of dark energy and the universe’s fate.
Cosmological Models: Shifting Paradigms
As new data minimizes the certainty surrounding the cosmological constant, cosmological models are facing potential paradigm shifts. The findings from DESI prompt a re-imagination of how we approach theories about the universe’s expansion. With dark energy potentially weakening over time, existing frameworks must adapt to reflect these revelations and consider alternative theories that could better explain our observations.
Engagement with novel hypotheses and models reflects ongoing advancements in cosmological understanding. The scientific community is encouraged to embrace flexibility and adaptation, exploring new models that encompass the implications of a dynamic dark energy. This evolution in thought signifies a crucial stage in astrophysical research, where theories must align with innovative findings, ensuring that our understanding of the universe remains enriched and responsive.
Understanding the Cosmic Web Through DESI’s Lens
The complex architecture of the cosmic web—a large-scale structure of the universe—is increasingly being revealed through DESI’s expansive mapping efforts. As researchers analyze the distribution of galaxies and clusters across vast distances, insights into the cosmic web provide a vital context for understanding dark energy’s impact on the universe’s acceleration. Each new discovery contributes a thread to the intricate tapestry of cosmic evolution.
By studying the dynamics of the cosmic web, scientists can gain a more nuanced view of how dark energy influences the structure and expansion of the universe. This interconnectedness reveals profound implications for future astrophysical research and our understanding of matter’s role within this web. Insights gleaned from DESI’s work not only illuminate dark energy but also contribute significantly to the ongoing quest to depict the universe’s story.
Future Directions in Dark Energy Research
As the DESI collaboration continues its mission, the future of dark energy research looks promising. With each night of observation, astronomers are poised to uncover new layers of information that build upon the groundbreaking findings already achieved. These efforts offer valuable potentials for answering fundamental questions about the fabric of the cosmos, deepening our understanding of dark energy, and its role in shaping the universe’s journey.
As technology advances and datasets grow, researchers are likely to explore innovative modeling techniques that could lead to more refined interpretations of dark energy’s changing nature. Moreover, ongoing studies in astrophysics, enriched by the input from DESI findings, will open up new investigative paths, integrating dark energy analysis with broader cosmological frameworks. This forward momentum ensures that the mystery of the universe remains a captivating endeavor for current and future generations of scientists.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dark energy analysis and why is it important for universe expansion?
Dark energy analysis focuses on understanding the mysterious force that drives the accelerating expansion of the universe. This analysis is crucial as it helps scientists explore potential changes in dark energy, providing insights into the universe’s fate and its fundamental physics.
How does the DESI collaboration enhance our understanding of dark energy findings?
The DESI collaboration plays a pivotal role in dark energy findings by creating detailed 3D maps of the universe. By analyzing the distribution of over 14 million galaxies and quasars, DESI helps researchers assess the impact of dark energy over billions of years, potentially revealing significant shifts in its influence.
What role does the cosmological constant play in dark energy analysis?
The cosmological constant is a theoretical framework used to explain dark energy’s role in universe expansion. Dark energy analysis examines whether this constant remains unchanged or evolves over time, which could lead to significant revisions in our understanding of cosmological models.
What are the recent discoveries in dark energy analysis from the DESI project?
Recent discoveries from the DESI project suggest that dark energy might be weakening, challenging previous assumptions that it behaves uniformly. This analysis, based on three years of data, indicates that the nature of dark energy may change, necessitating an update to the standard model of cosmology.
How does dark energy influence the structure of the universe?
Dark energy influences the structural formation and evolution of the universe by accelerating its expansion. Understanding this influence through dark energy analysis helps astrophysics researchers investigate how galaxies and cosmic webs are shaped over time.
Why is the study of Baryon Acoustic Oscillations significant in dark energy analysis?
Baryon Acoustic Oscillations provide a crucial standard ruler for measuring cosmic distances, which is essential in dark energy analysis. By analyzing these patterns, researchers can track how dark energy’s effects have changed over the universe’s history.
How can the public engage with the findings of dark energy analysis from DESI?
The public can engage with the findings of dark energy analysis from DESI through the Data Release 1, which allows access to detailed information on celestial objects. This dataset supports educational and research initiatives, making dark energy insights more accessible to everyone.
What is the future of dark energy research following the DESI collaboration results?
The future of dark energy research is poised for exciting developments following DESI’s findings, as ongoing analysis may lead to a deeper understanding of the universe’s fate. Researchers will continue to explore potential fluctuations in dark energy, potentially revolutionizing our cosmological perceptions.
| Aspect | Key Points |
|---|---|
| Collaboration | The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) involves over 900 researchers from more than 70 institutions worldwide. |
| Primary Findings | New research suggests that dark energy may be weakening over time, challenging the cosmological constant theory. |
| Research Method | DESI has created the largest 3D map of the universe, examining its impact over the past 11 billion years. |
| Key Contributors | Key members from Harvard, including Professor Daniel Eisenstein, contributed to algorithm development and cosmological interpretations. |
| Public Engagement | DESI Data Release 1 is available for public exploration, aiding in broader astrophysical research. |
| Future Research | Continuing to investigate galaxy evolution, the cosmic web, and the universe’s structure alongside dark energy studies. |
Summary
Dark energy analysis has revealed significant insights that may reshape our understanding of the universe’s expansion. Recent findings from the DESI collaboration indicate a potential weakening of dark energy, which challenges the long-standing notion of it as a constant force. With contributions from prominent researchers and the development of extensive datasets, this research not only enhances our grasp of cosmological phenomena but also sets the stage for future inquiries into the fundamental driving forces of the universe.