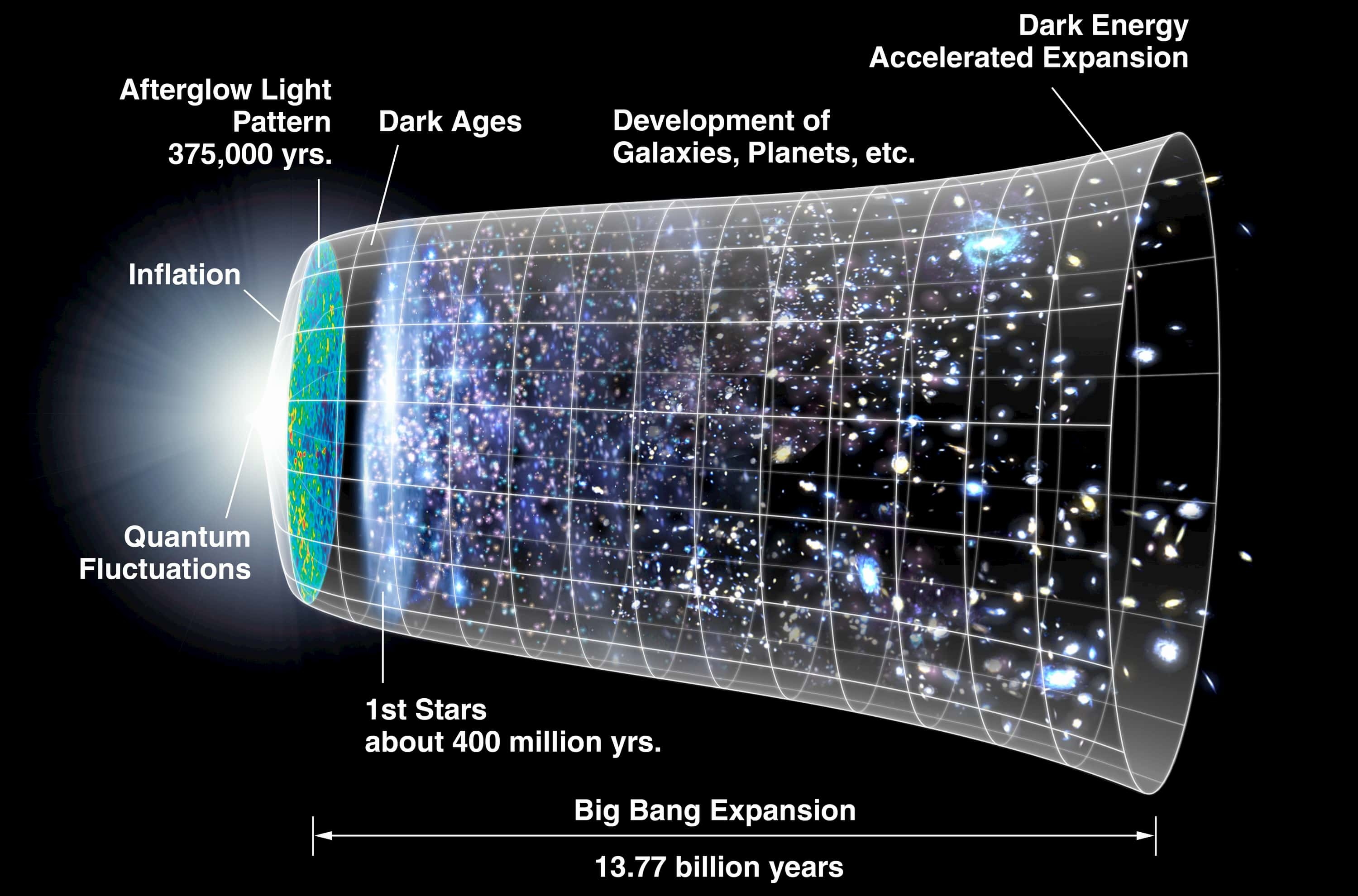
Dark energy plays a pivotal role in understanding the universe, as it is believed to be the mysterious force behind the universe’s accelerating expansion. Recent insights from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) collaboration have sparked intriguing discussions about the nature of dark energy, suggesting that this cosmological constant may not be as constant as once thought. By analyzing a monumental 3D map of over 14 million galaxies and quasars, researchers aim to uncover variations in dark energy’s influence across billions of years. The latest findings from DESI not only challenge existing theories but also open new avenues for dark energy analysis, potentially reshaping our comprehension of galaxy evolution and the cosmos itself. As astronomers interpret DESI results, the implications for the future of the universe come into sharper focus, urging the scientific community to reevaluate fundamental cosmological models.
The enigmatic phenomenon of dark energy, often referred to as the force driving the cosmos apart, is at the forefront of contemporary astrophysical research. As scientists delve into the intricacies of this galactic enigma, terms such as the cosmic expansion and cosmological dynamics come into play, shedding light on how this force shapes the universe. The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) embodies a critical tool in unraveling the complex tapestry of the universe’s evolution, enabling detailed studies of the distribution of matter over time. By employing a vast array of data gathered from distinct celestial phenomena, researchers can ultimately discern how variations in this enigmatic force affect the cosmos. Dark energy, its effects, and the resulting revelations present a captivating narrative that continues to evolve alongside our understanding of the universe.
Understanding Dark Energy and Its Role in Universe Expansion
Dark energy is a mysterious force that is largely responsible for the accelerating expansion of the universe. Initially thought to be a constant force, like a cosmological constant, new findings suggest that dark energy’s influence may be diminishing over time. This notion arises from groundbreaking studies associated with the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) which are redefining our understanding of cosmic dynamics. Despite its elusive nature, understanding dark energy is crucial for predicting the ultimate fate of the cosmos and has become a pivotal focus of modern astrophysical research.
The effects of dark energy are profound as they influence the rate at which our universe is expanding. Researchers, utilizing groundbreaking methodologies like those involved in the DESI analysis, have begun to observe potential shifts in dark energy’s behavior over billions of years. By mapping the 3D distribution of over 14 million galaxies, scientists are piecing together a complex puzzle that sheds light on how dark energy has evolved, possibly indicating that our present cosmological models are in need of an update.
The Impact of DESI Results on Cosmological Constant Theories
The recent findings from the DESI collaboration have sparked conversations about the reliability of the cosmological constant as a definitive explanation for dark energy. Traditionally, the cosmological constant is viewed as a static force; however, the disturbing possibility that it might change over time could shift paradigms in cosmology. The detailed observations made by DESI not only provide a more comprehensive view of the universe but also challenge long-standing assumptions about how cosmic forces operate.
By analyzing patterns left in the universe’s early mass distribution, researchers have identified changes in dark energy’s effectiveness over 11 billion years. These insights may indicate that rather than being a fixed entity, the cosmological constant is an adaptive force that evolves with the universe. This revelation can lead to new theories that incorporate dynamic changes rather than relying on static interpretations, fostering further studies into the fundamental nature of dark energy.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is dark energy and how does it relate to the cosmological constant?
Dark energy is a mysterious component of the universe that is believed to drive its accelerating expansion. It is often associated with the cosmological constant, which is a term in Einstein’s equations of General Relativity that describes the energy density of space. This constant is thought to be responsible for the observed repulsive force that is causing galaxies to move apart.
How do DESI results contribute to our understanding of dark energy?
The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) provides crucial data for analyzing dark energy by creating the largest 3D map of the universe. Recent DESI results suggest that dark energy may be evolving over time, which challenges existing theories about the accelerating expansion of the universe and the role the cosmological constant plays in it.
What impact does dark energy have on the expansion of the universe?
Dark energy affects the rate of expansion of the universe by exerting a repulsive force that counteracts gravitational attraction. This force is believed to dominate the universe’s energy density, leading to its accelerated expansion, which researchers are currently examining through studies like DESI.
How do baryon acoustic oscillations relate to dark energy analysis?
Baryon acoustic oscillations are periodic fluctuations in the density of visible matter in the universe. These patterns serve as a cosmic ‘ruler’ that helps scientists measure the expansion history of the universe, allowing for better analysis of dark energy’s influence over time, as elucidated in DESI’s findings.
What implications do the latest DESI results have for our understanding of galaxy evolution?
The findings from the DESI collaboration suggest that as dark energy evolves, it may influence the way galaxies are formed and evolve. This research sheds light on the connection between dark energy and the distribution of galaxies on cosmic scales, potentially altering existing models of galaxy formation.
Why is the study of dark energy important for cosmology?
Understanding dark energy is crucial for cosmology because it governs the fate of the universe. It affects the rate at which the universe expands and influences the overall structure of cosmic evolution. Insights gained from research like DESI inform our fundamental understanding of physics and could lead to significant revisions of current cosmological models.
| Key Points | Description |
|---|---|
| International Collaboration | The Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) involves over 900 researchers from over 70 institutions. |
| Dark Energy Research | Recent findings suggest dark energy may be weakening, impacting our understanding of the universe. |
| Historical Analysis | The study utilized the largest 3D map of the universe over the past 11 billion years, examining baryon acoustic oscillations. |
| Significant Contributions | Harvard researchers played a key role, from developing algorithms to public outreach. |
| COSMOS Data Access | DESI Data Release 1 is publicly available for exploration of millions of celestial objects. |
| Ongoing Research | The DESI survey continues, enhancing the understanding of galaxy evolution and cosmic structures. |
Summary
Dark energy, a fundamental concept in modern cosmology, is pivotal for understanding the accelerating expansion of the universe. Recent findings from the Dark Energy Spectroscopic Instrument (DESI) reveal that the properties of dark energy could be changing, which may necessitate revisions to existing cosmological models. This ongoing research not only enhances our comprehension of the universe’s fate but also contributes significantly to the fields of galaxy evolution and cosmic structure. As scientists continue to uncover the mysteries surrounding dark energy, the insights gained could reshape our fundamental understanding of the cosmos.